What is the Pipe Fabrication (piping spool)?
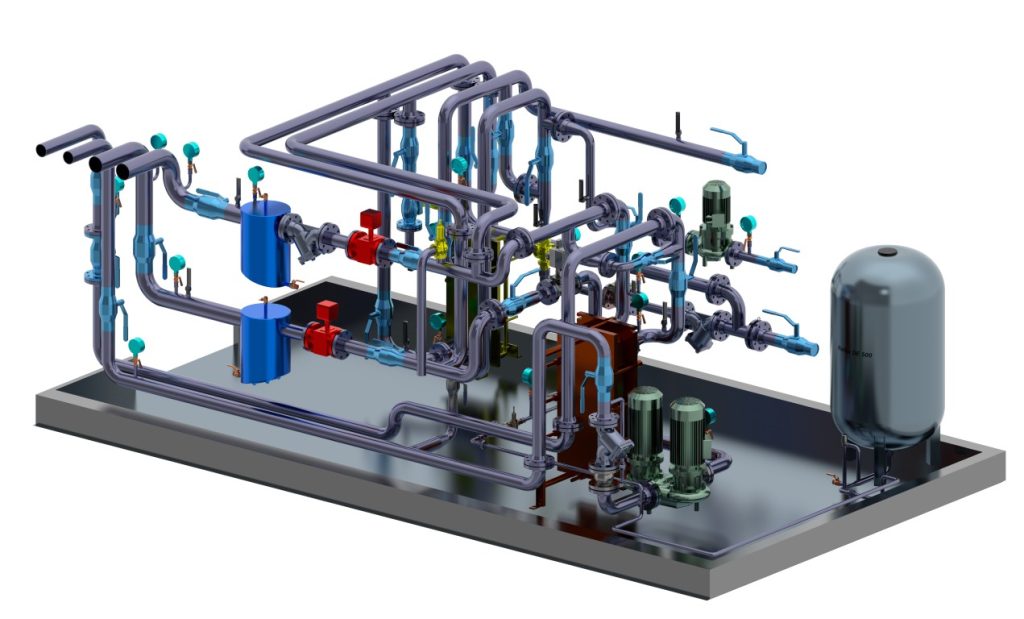
Pipe fabrication is the process of transforming raw pipes and fittings into a complete piping system that meets specific requirements.
It involves cutting, bending, welding, and assembling pipes and fittings of various sizes and materials to create a network that can transport liquids, gases, or solids.
It is a harmonious blend of art and engineering, a process where raw materials are transformed into pipelines specifically designed according to the demands of different applications.
Moving beyond its utilitarian roots, it plays a key role in shaping material and process flows in industries such as automotive, agricultural machinery, maritime industry, and construction.
Forget about putting pipes together.
Pipe manufacturing is more like breathing life into metal, transforming raw materials into the complex and vital arteries that carry the foundations of our modern world.
It is a blend of precision, craftsmanship, and problem-solving where skilled hands transform plans into tangible systems that whisper efficiency and reliability.
What makes pipe manufacturing different is the method of customization.
Each project requires a unique model of pipe and fittings to navigate tight spaces in power plants or overcome complex flow challenges in industries.
Unlike stereotypical solutions, fabricated systems are custom-made to specific needs such as pressure, temperature, and flow, guaranteeing the highest performance at every twist and turn.
But it’s not just about functionality. In the hands of creative minds, even exposed pipes can become an art form.
Architectural spaces get a touch of industrial elegance with beautifully crafted pipes, adding a unique character to the design.
This is a testament to the craft’s versatility and showcases its ability to seamlessly blend form and function.
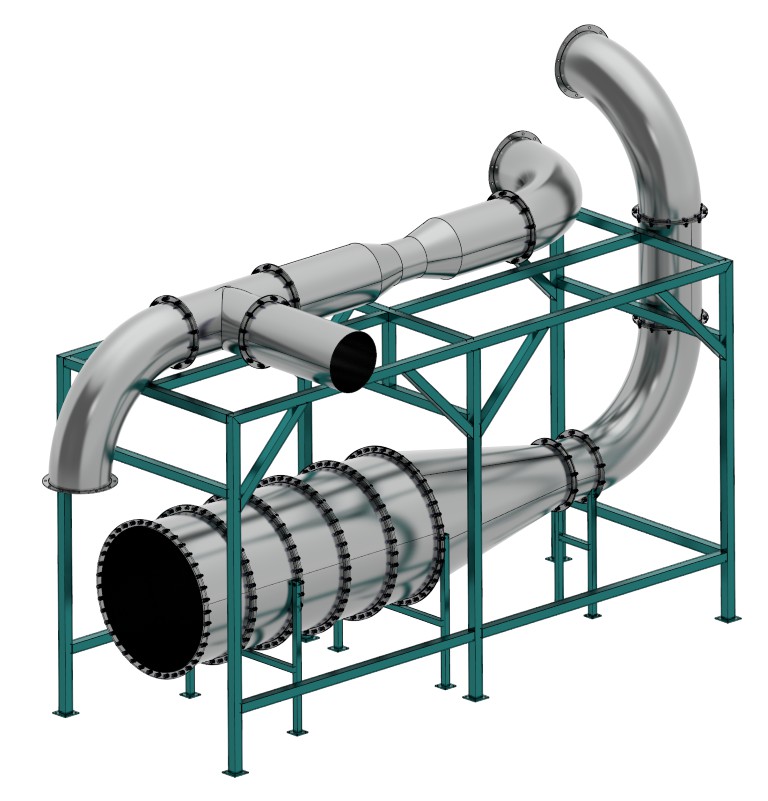
Two Types of Pipe Manufacturing
Pipe manufacturing is divided into two categories.
These categories are based on location of production. It can be shop manufacturing or field manufacturing.
Where the pipe will be installed or manufactured may depend on several factors.
Factors include profitability, convenience, nature of the job, accessibility of materials, equipment, and more. Both types have advantages and disadvantages.
Shop Fabrication (prefabricated piping spools)
In this type of pipe manufacturing, manufacturers carry out the design, manufacturing, testing and painting processes in the pipe facility.
Professionals then transport the assembled reels to construction sites.
The main features of workshop manufacturing are:
* Manufacturers use high quality materials.
* Workshop manufacturing ensures accuracy due to controlled environment.
* Labor costs in workshop manufacturing are lower than field manufacturing.
* Efficiency in shop manufacturing is higher compared to on-site manufacturing.
* Mobilization costs in workshop manufacturing are lower than in field manufacturing.
* Safer and more convenient than field fabrication.
* Pipes are produced ahead of their time. Less likely to be late at work.
Pipe fabrication in a Shop (prefabricated piping spools)
The pipe manufacturing process requires the pipes and pipe fittings to be assembled according to the spool drawing.
Pipe manufacturers must consider installation size and potential problems with transportation.
For example, Subassemblies can be an effective transportation method.
The following steps highlight pipe fabrication;
1. Cutting and Marking: Marking is done as per design drawing requirements and supervisor verifies it before cutting.
2. Tagging: Pain marking, dye stamping, or Tagging–pipe heat numbers are added to the cut pieces before cutting the pipe.
3. End-Prep: End preparation (beveling) and fit-up are performed following an approved Specification and WPS.
4. Welding of Pipes: In butt welded joints, care should be taken to ensure that the longitudinal seams of the pipes do not come in a single row.
The seams need to clear the branch connections and be at least 100mm apart.
It is important to ensure that longitudinal seams do not rest on the steel structure
5. Welding Fittings and Pipes: Pipes and Fittings for fit-up are placed on a temporary pipe bed, and supports are secured.
The arrangement is then inspected for quality Fit-Up.
Once inspection clearance is received, Qualified welders weld joints.
6. Marking Details: Various details line pipeline No., Component Heat No., Joint No., Assembly inspection signature, Welder No., Visual inspection signature and welding date are marked near the joint using a metal paint pen.
— The Spool Number on the pipe is marked with a crayon and an aluminum label is attached to the spool
7. Heat-treatments: Preheating and PWHT will be done at the shop or field as per project-specific requirements.
8. Inspections: NDT testing, which is very important for pipe manufacturing, is carried out according to the project specifications or guidelines.
Once permission is received, the reels are released with a release tag for assembly/painting.
— Rejected Spools are identified by yellow and black labels and sent for repair work and must undergo NDT
9. Documentation: Field inspections for quality control purposes after painting and recording in the prescribed format.
After the painting check, the reel is released for assembly.
10. Stainless Steel Pipe Fabrication: Stainless steel piping fabrication is performed in the shop in an isolated area from carbon steel and alloy steel.
The equipment and tools used for Carbon Steel fabrication should not be used for Stainless Steel.
Stainless steel tools are used for brushing, grinding, clamping, etc.
11. Protection: For temporary storage and safety installation, all completed pipe spools with flanged raised surfaces shall be fitted with plywood bulkheads and spool ends shall be fitted with good covers.
Gallery;










