A modular process skid is a process system housed in a frame that allows easy transportation of the processing system (skid assembly). Individual skids can include complete process systems, and multiple process skids can be combined to create larger process systems or entire portable plants. Sometimes these are called “systems in a box”. An example of a multi-skid process system may include a raw material skid, an utilities skid, and a processing unit working together.
Process skids are considered an alternative to traditional stick-built construction, where process system parts are shipped individually and installed incrementally at the production site. These provide the advantage of parallel construction, where process systems are built off-site at a manufacturing facility, and construction site improvements are completed simultaneously at the facility site. Slides are not always convenient. If individual process parts are large and cannot reasonably be contained within the modular process skid frame, traditional construction methods are preferred
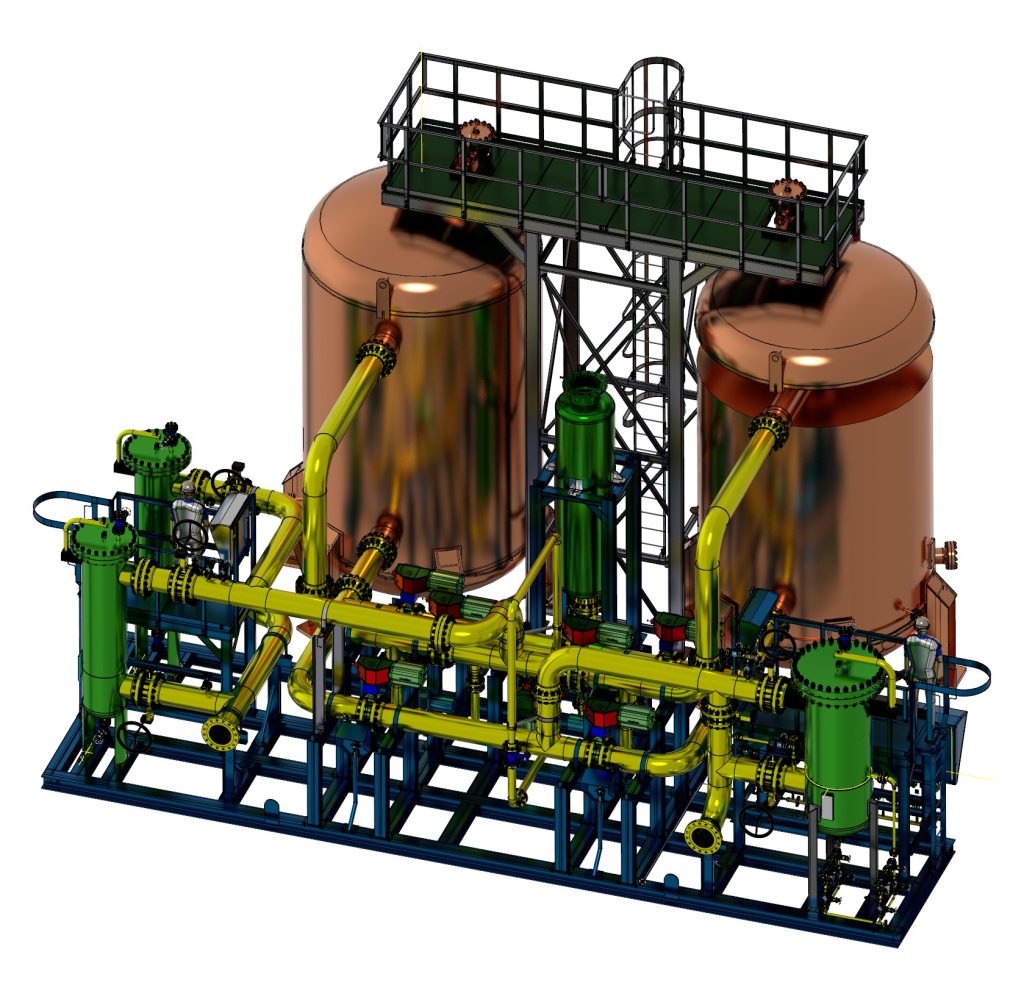
Skid design and layout
Portable design – because they are self-contained units built within frames, skid systems are easier to transport than traditional process systems
Small footprint – process skid frames allow equipment to be layered. Pipes, tanks, and necessary process equipment can be fitted into a smaller space with the skid design.
Consolidated process connections – process connections are concentrated in a single point on the skid, simplifying plant connections. In traditional process systems, connections are spread throughout the plant.
Controlled assembly – skids are often built off-site in controlled conditions. Existing operations are not affected by skid production.
FAT testing before installation – Factory acceptance testing (FAT) can be completed before modular process skids are shipped to the field. This reduces on-site startup time.
Accessible layout design – skids are designed for accessibility; usually include a center aisle and the main pieces of equipment are placed on the edge of the frame.
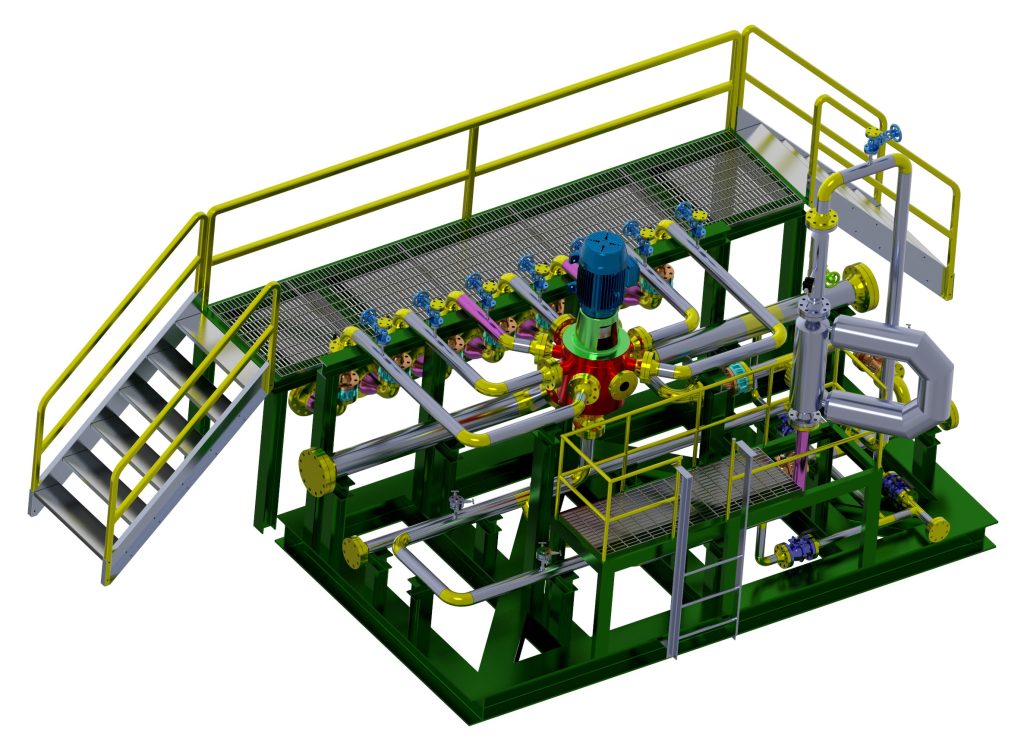
Skid applications
• Batch processing
• Bio waste deactivation systems
• Centrifuge systems
• Chemical processing
• Chemical reactors
• Clean-in-place systems
• Coating systems
• Continuous production systems
• Demonstration plants
• Distillation
• Furnaces or Fired Heaters
• Flavor mixing
• Food and beverage processing
• Fuel delivery systems
• In-line blending systems
• Mixing systems
• Perfume mixing
• Petroleum processing
• Pilot plants
• Processing plants
• Pump carts
• fluid process
• Raw materials processing
• Refining
• Wastewater treatment systems
Gallery;







